By Hassan Idris
Discussing trending and contentious topics has never been my preferred inclination, not because of a lack of opinions or the ability to articulate them but rather due to the potential conflicts it may engender with those who hold me in high esteem. Nonetheless, today, I shall delve into the trending and contentious subject matter that has generated a whirlwind of discourse on social media, polarising individuals along sectarian, regional, and religious lines and culminating in mutual vilification.
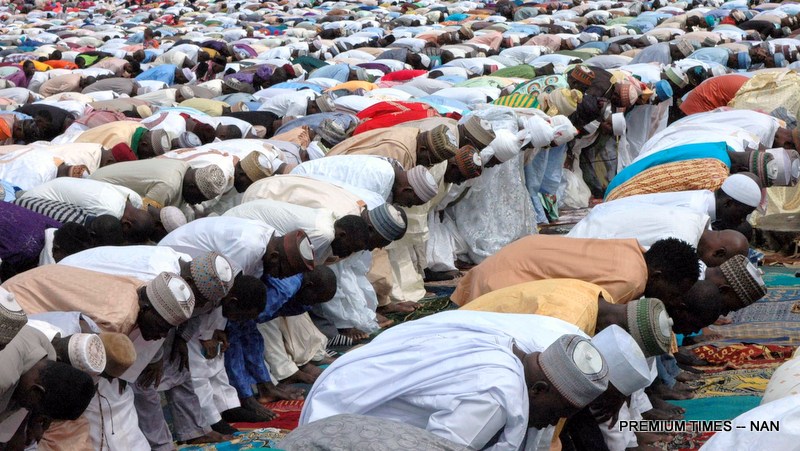
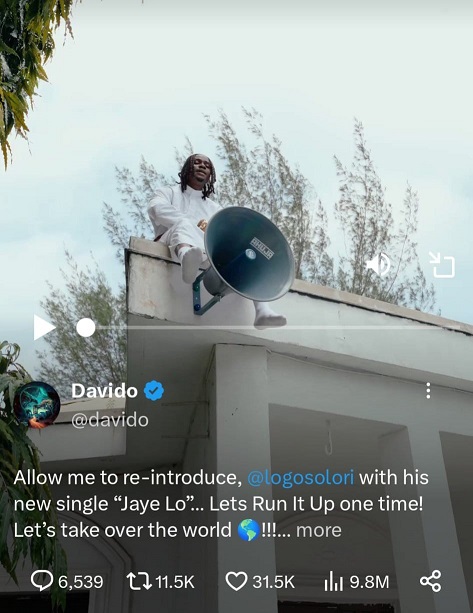
Specifically, I aim to scrutinise the 45-second video released by the Nigerian music sensation David Adeleke, famously known as Davido. In this video, men donned in white jalabia and caps dance boisterously in front of a mosque immediately after partaking in prayers. Adding further intrigue, Logos Olori, Davido’s protege, occupies a prominent spot atop the building’s roof.
Notably, even though the singer makes mention of the phrase ‘Alhamdulillah’ (praise be to God), the video and the accompanying song have been met with severe disapproval from many Nigerians and fans, particularly among the Muslim community, who perceive it as an affront to Islam. They vehemently demand an apology, accusing Davido of disrespecting their religious practices by intermingling sacred rituals with song and dance.
Despite the mounting pressure, Davido finally relents and takes down the video after two days of receiving criticism, opting for a predominantly silent stance and refraining from issuing formal apologies. Notably, Professor Wole Soyinka, in a surprising twist, urges Davido not to apologise for releasing the ‘Jaye Lo’ video, asserting that dancing in front of the mosque does not possess the provocative connotation purported by some.
Among the voices calling for an apology from Davido are prominent Muslim faithful such as Ahmad Ganga, Ali Nuhu, Ashraf Yaman, Ayaat Saeed, Basira Ugochi, and numerous others. Conversely, some Muslims have countered this demand, contending that the singer’s lyrics and actions did not overtly denigrate the Islamic faith. Furthermore, they argue that the video was not intended to ridicule Islam but reflected a cultural norm in Yoruba society.
Additionally, they highlight the existence of Islamic sects, such as the Tijjaniya and Shi’ite, in the northern region, who employ the Mandiri drums as part of their worship practices, thus, indicating that some Muslims themselves engage in similar expressions of religious celebration, with no objections from the community. Before delving into the sociological perspective of religion, it is imperative to recognise the profound significance of religion, particularly in Africa. For many Muslims, it is not merely the song or the jalabiya donned in the video that raises concern, but rather the potential mockery of prayer, a cornerstone of Islam, considered sacred and inviolable. It stands in stark contrast to profanity and warrants utmost respect.
Comparatively, other musicians like Naira Marley may espouse diverse perspectives, yet their words do not evoke similar anxieties. For instance, Naira Marley’s song proclaims, ‘God is the driver, while the Prophet (SAW) is the conductor,’ which, despite its unconventional nature, does not overtly trivialise prayer. Indeed, if Naira Marley had ventured into such territory, he would likely have faced a similar backlash. In response to the contention that some Islamic sects might engage in activities akin to the video’s content, it is essential to discern that while various expressions of worship exist, dancing during prayers remains absent from any Islamic sect. Moreover, the significance of the mosque, as elucidated in the Qur’an, holds paramount importance for Muslims, who regard it as the most sacred and cherished space in their lives. Thus, actions that appear to contradict the mosque’s sanctity are naturally met with vehement objection.
As for Professor Wole Soyinka’s intervention, his failure to fully grasp Nigeria’s religious and multicultural fabric, coupled with his atheistic beliefs, may have influenced his hasty entry into this contentious issue without considering the multifaceted perspectives. Thus, there seems to be an underlying layer of ethnocentrism at play, though it is crucial to clarify that this observation is not intended to belittle Soyinka in any manner.
Turning our attention to Durkheim’s Elementary Forms of Religious Life, the philosopher Charles Taylor’s elucidation of religion as a comprehensive system of beliefs and practices encompassing human existence and its relation to the ultimate conditions of being and other human beings presents a multifaceted framework for analysis.
Durkheim’s seminal work contends that religion is not confined to individual beliefs and practices but rather constitutes a sociological phenomenon that both shapes and is shaped by society. Central to his argument is the concept of ‘collective representations,’ which denotes shared symbols and ideas that foster cohesion among individuals, binding them together in a collective community. Collective effervescence, a cornerstone of religious experience according to Durkheim, entails the shared emotions and sense of unity that emerges when people unite for a common purpose, often manifested in rituals and communal activities.
Furthermore, Durkheim’s delineation of the ‘sacred’ and the ‘profane’ elucidates the fundamental distinction between holy or special elements (the sacred) and the mundane aspects of everyday life (the profane). The video in question seemingly breaches this sacred-profane dichotomy, incorporating elements considered sacred within a context that may trivialise their significance. To elucidate the connection between Durkheim’s ideas of the sacred and the profane, the concept of totemism emerges as an essential component of his thesis.
Totemism encompasses groups of individuals coalescing around a common totem, an emblematic object or animal that symbolises the collective community. The totem, imbued with sacredness, serves as a focal point in rituals and ceremonies, forging a shared sense of identity and unity within the group. By drawing this parallel, the video can be perceived as appropriating religious attire and symbols, potentially attenuating their original sacred import.
Moreover, Durkheim’s concept of ‘mana’ merits consideration of the video’s content. Mana constitutes a spiritual force or energy believed to inhabit sacred objects or spaces. Often linked to animism, the notion that objects and locations possess spirits or souls, ‘mana’ illustrates how the sacred imbue objects and places with special significance. Here, the video’s portrayal of dancing immediately after prayers may be construed as desecrating the sacredness associated with the mosque. As Durkheim transitioned his focus to modern societies, the idea of ‘mechanical solidarity’ comes into play, wherein traditional societies cohere through shared values and beliefs among relatively homogeneous groups.
Comparatively, ‘organic solidarity’ characterises contemporary societies, wherein specialised social bonds form through the division of labour, with various individuals and groups performing distinct functions. The video, juxtaposing modern entertainment (the dance) within the context of a sacred religious space, potentially mirrors the fragmentation and diminished shared values observed in present-day society, evoking notions of anomie.
As a sociologist and poet, I believe some may perceive the Muslim community’s response to Davido’s music video as an overreaction. While concerns are warranted, approaching the issue with knowledge and wisdom, as instructed in the Qur’an, would have been more constructive. Addressing Davido’s actions maturely and knowledgeably could have fostered a more amicable resolution. However, amidst the controversy surrounding the video, it is crucial not to lose sight of the pressing issues in the North, such as kidnapping, terrorism, and poverty, which demand urgent attention and resolution. Calling for uniformity in addressing these challenges alongside the concerns over the music video could have a more significant impact in addressing social issues and fostering a sense of collective responsibility.
Furthermore, it is essential for everyone, regardless of their religious background, to respect and understand the beliefs and cultures of others. Ethnocentrism and a lack of cultural relativity can perpetuate societal misunderstandings and divisions. Respect for all religions, and their sacred practices, should be upheld, emphasising the need for mutual understanding and harmony among diverse communities.
In conclusion, when scrutinising Davido’s music video from a Durkheimian sociological perspective, many potential issues concerning the sacred and the profane in religion emerge. The video’s portrayal of dance immediately after prayers and its use of religious symbols may be perceived as disrespectful and culturally insensitive by some Muslim community members. Moreover, its potential impact on social cohesion and integration in Nigeria’s diverse and multicultural society warrants introspection. Both sociologists and individuals must remain cognizant of religious sensitivities while striving for a profound understanding of different religious practices, fostering mutual respect and harmony within society.
While the controversy surrounding Davido’s music video persists, individuals and communities must engage in constructive dialogue, foster mutual respect, and address societal challenges with collective responsibility. Religion is paramount. It should be treated with reverence, regardless of the particular faith. Let us strive to uphold the principles of knowledge, wisdom, and cultural relativity in our interactions, aiming for a more cohesive and harmonious society. May we all be guided right in our actions and decisions.
Hassan Idris is a Sociologist & Poet and can be contacted via idrishassan25@yahoo.com.