By Prof. Abdalla Uba Adamu
Hausa Intangible Heritage Revival – Overture to the Symphony
When Gillian Belben, the British Council’s new Director in 2004, wanted to introduce a truly unique project in enhancing the cultural relations between Britain and Nigeria, a series of initiatives were proposed. One of them was Connecting Futures – a project that linked youth in Britain and Nigeria through music, films, debates, social advocacy and the arts.
I was involved in the film and music projects. In the music domain, we wanted to create a music ensemble that would revolutionize traditional Hausa music – an endangered performing art. The reason for its endangerment was its griot-based nature. Traditional Hausa musicians were seen basically as praise singers – singing the praises of rich, famous, infamous patrons who pay them a lot of money. The changing Hausa society in the 21st century saw the disappearance of such griot musicians – as no one had the money (or the gullibility) to pay to hear their praises, except politicians – thus making such performances short-lived and, fundamentally, non-artistic. I was the Chairman of the defunct Center for Hausa Cultural Studies, based in Kano. The Center and the British Council liaised to develop a project to create a sustainable focus for Hausa traditional performing arts, at least for as long as the Connecting Futures project lasted. There was no government input in this – we did not seek any, nor do we expect any, despite the existence of the History and Culture Bureau (HCB) in Kano.
Gillian and I were interested in contemporary European music of multiple-instrument ensembles and decided to recreate an ensemble of Hausa musicians playing different instruments. This was unheard of in Hausa ethnomusicology since, traditionally, Hausa griot musicians tended to stick to only one instrument (stringed or percussion). However, with the advent of ‘modernity’ in traditional performing arts, some Hausa club musicians started combining string instruments (kukuma mainly) with percussion – drums and calabashes. Examples include Garba Supa and Hassan Wayam. For more on this, see Jacqueline Cogdell DjeDje’s brilliant Fiddling in West Africa.
We were not interested in modern synthesizer music with its sampled sequencers of sounds that modern Hausa ‘nanaye’ singers arrange to form melodies and then transposed lyrics over the beat, often with female autotuned voices – all mimicking Indian film soundtrack singers. This production mode earned their genre the name of ‘nanaye’ – girlish (not female, incidentally!) music.
In our project, we envisaged four different instruments working in harmony to produce at least an acceptable ‘post-modernist’ Hausa traditional griot music – without the praise singing. We sent out notices requesting expressions of interest from interested musicians, mainly griot. Many ‘nanaye’ singers came, and we turned them away – we wanted musicians, not singers –none of the nanaye singers could play any traditional instrument. Auditions were held with those who can play a specific traditional instrument, and we first chose three: sarewa (flute), kukuma (fiddle), and kalangu (drums). Because there were many varieties of drums, we added duman girke ‘conga’ drums. All were to be played by males, as was traditional in Hausa traditional performing arts. That was when Gillian decided to up the ante by insisting on a female musician join the four young men.
This was a tall order for many reasons. Hausa women are not accustomed to playing musical instruments, especially in public. There were, of course, exceptions. The late Hajiya Sa’adatu Barmani Choge and Hajiya Uwaliya Mai Amada both had ‘calabash orchestras’ and performed in public. You can find further readings on her life and performance at the end of this. Currently, in 2022, Choge’s children and former bandmates have continued the tradition of performing in public – mainly at weddings and naming ceremonies. They used to perform during political campaigns, but the bad publicity and accusations of improper behaviours put paid to that.
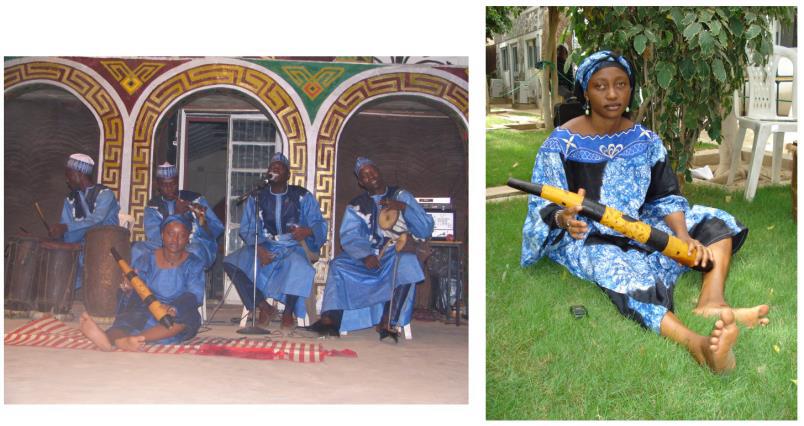
Both Uwaliya and Barmani were in advanced age and could get away with pretty much everything. Getting a young Muslim Hausa woman to join young males and perform in public was genuinely challenging. However, Gillian was determined to do it, so we focused on the instrument the female band member could play. The only viable one was shantu – an aerophone. This was a female musical instrument, which, together with the bambaro (mouth harp), has all but disappeared.
Eventually, we found Fati Ladan, a lady living in Kano but originally from Niger State, who was one of the ƙoroso dancers attached to the History and Culture Bureau (HCB), Kano. The HCB already have a shantu ensemble, made up of much older women who perform during opening ceremonies at government events – adding a bit of classic flavour to the settings before the long speeches start.
Fati could not play the shantu herself but was willing to learn, especially from the existing shantu ensemble at the HCB. She eventually became adept at it. In the next stage of our project, we added her to the earlier group of four male musicians and called the group Arewa. But since the fronts man of the band was Nasiru Garba Supa, the son of the legendary kukuma player, Alhaji Garba Supa, we later referred to the band as Nasiru Garba Supa and Arewa. You can watch Fati’s solo performance, which I recorded and edited in 2014 in Kano, at https://bit.ly/3DF1Hfk.
The shantu, a percussion tube used by Hausa women, found its way to North Africa due to the trade in enslaved women (for more, see Ames and King, Mercedes). The Kanuri ganga (double-headed cylindrical drum) and the Hausa and Songhai instruments of the same name are North African borrowings from West Africa. An extremely large variant of the shantu, called languru (sharing a name with a language learning and dictionary app) and also referred to as shantu, is played by male Fulɓe.
Interestingly, the languru is similar to the alphorn, a wind instrument that is a national symbol of Switzerland. It has been used by Alpine farmers for hundreds of years as a form of communication in mountainous regions, although now it is simply a musical instrument. During the 18th centuries it was regarded as a beggar’s horn, since it was most often played by impoverished shepherds in the cities, obviously using smaller versions. The Fulɓe languru is also a wind instrument and played during festivities in gatherings of the Fulbe in the evenings after the cattle has been squared away either in corrals or designated areas. The smaller shantu used by women is a tubular shell of a long, narrow gourd, open at both ends; often decorated with patterns burned on, or cut into, the outside shell. It is held in the right hand and beaten in a variety of ways by the seated player, including the following:
- Stamped with its lower end against the inside of the right thigh, or against the calf of the right leg.
- Stamped with its upper end against the open palm of the left hand
- Tapped with its outer shell against the shin bone of the right leg
- Tapped with the lip of its lower end against the ground
- Tapped on its outer shell with rings on the fingers of the right or left hand
- Used singly or with one or more other shantuna in the statement of zambo (innuendo), as in waƙar kishiya (song of co-wife), karin magana (proverbial sayings), etc., through the imitation of speech tone and quantity; used solo or with one or more other shantuna in the accompaniment of song
- Used by women for social comment (e.g., by a co-wife in criticism of her partners) or for informal music-making.
Nasiru Garba Supa’s Arewa and Fati performed many concerts for the British Council over a period of two years, generating a lot of interest and accolades due to Fati’s often solo slot given during any performance. Since the concerts were family affairs – involving the whole family to attend – many young people were fascinated by Fati’s shantu playing.
Gender Rebellion and Shantu music – The QAC Troupe in Historical Perspective
Generally restricted mainly to elderly women playing it to amuse themselves, the shantu was made a choice of musical performance in all-female secondary schools in northern Nigeria in the 1970s. For the most part, they performed during school activities – graduation, cultural days, national events, etc. Once the students graduate from the secondary schools, they simply retire the shantu to what would pass for attic. However, perhaps remembered by people in their sixties, the prominence of shantu as an instrument in public performance was catapulted into legitimate public entertainment in the early 1980s by students of Queen Amina College (QAC), located in Kakuri, Kaduna, northern Nigeria, especially the 1984 graduating class. They were encouraged to use it as part of the then cultural revival in secondary schools. The main reason for their popularity was rehearsed perfection. Perhaps not surprisingly, they were more frequently featured on NTA Kaduna cultural variety shows.
However, soon enough they started drawing criticisms due to their increasingly bold, and what was seen as anti-cultural, performances. Perhaps carried away by their popularity, they became more experimental in their choreography. One of the performances on their setlist was Gantsare Gaye. Accompanied by the deep bass-like hollow sound of about 10 shantus, the dancers energetically move their derrières in an obscene movement of sexualized dance routine (mainly referred to as ‘gwatso’/thrust). Although the 1980s was a liberal decade (and almost twenty years before Sharia was launched in Islamicate northern Nigeria), the sight of teen girls performing such obscene dance routines on public Television drew critical reaction and condemnation in newspapers and from Muslim clerics in Kaduna and Kano. The QAC girls were undaunted, however, knowing fully well that they had the full protection of their powerful parents, the girls themselves eventually marrying into equally powerful influential homes, with quite a few of them becoming powerful themselves. QAC was an elitist school and thus created a cultural disjuncture in the performance of the girls. Interestingly, it evolved from a Catholic missionary educational tradition – thus giving multiple readings to the girls’ performances. The college was established as the Queen of Apostles College Kaduna by Catholic Missionaries in 1940, becoming Queen Amina College when it was taken over by the Kaduna State government in 1970s following government takeover of missionary schools.
Their defining creative moment was at the International Market for Film and Television Programmes, organized by the Nigerian Television Authority, held at Durbar Hotel, Kaduna, from 27th to 31st March 1983 (NTA IMPT ’83). Part of the festival included performances by various artists – and the QAC girls were requested to perform on stage for 15 minutes. Their troupe consisted of 22 performers – 12 call-and-response vocalists and dancers, and 10 shantu players who also called the chorus. There were no percussion instruments, with the bass sound of the shantu being sufficient enough.
Through trawling various Facebook postings, I have been able to identify some of the performers – now all grandmothers and in their mid-50s! They included Fatima Umar Wali, Halima Waziri Digma, Maryam Tinau, Maryam Adamu, Hauwa Suleiman, Aishatu B Musa, Rabi Tinau, Binta Tukur, Binta I Kaita, Fatima Musa, Fatima Usman, Mairo Mu’azu, Amina Musa, Zuwaira Abubakar, and of course, others, actually mentioned in some of the verses.
Their setlist for that festival was made up of five songs, plus intro and outro skits. The main songs were Karyamaye, QAC, Alhaji Lawal Kalabayye, Ko da Rabo, Gantsare Gaye. The song structure of their performance did not fall into the classic intro, verse, pre-chorus, chorus and bridge, associated with modern, basically English songs. They adopted the framework of chorus, verse, chorus – in a call-and-response pattern, typical of traditional songs in northern Nigeria. The chorus was also the song’s hook. Only one song had an opening doxology of one line (Karyamaye). Sleuthing on Facebook comments about the uploaded videos of the performances reveal that Alhaji Lawal Kalabayye was named after their food contractor! He apparently did a good job to warrant having a whole song devoted to him!
The opening song of the performance, after a few seconds of the intro skit, was their masterpiece: Karyamaye (a made-up word to provide vocal harmony). This was an invective song targeted at their public culture critics. The first (and actually, the main) verse is transcribed below:
To bismillah, jama’are, Arrahmani/People, we start in the name of Allah
Mu ƴan Hausa, da mu ƴan Shantu/We, the Hausa and Shantu club
Da ba ruwan mu da kowa/ Those who are not bothered
Ba ruwan mu da kowa/We are not bothered
Sai dai a gan mu a bar mu/See us, and leave us alone
Sai ko hararar nesa/Your dirty looks only at distance
A cikin duniyar nan, Wallahi/ In this world, by Allah
Muna da masoya, kana muna da maƙiya/We have fans and we have haters
An ƙi jinin mu, kamar a sa mana kananzir/They hate us, wishing to pour kerosene on us
A ƙyatta ashana a jefa/And lit [the fire to burn us]
Ba’a san mu kamar a kashe mu/The haters want to see dead
Ga rijiya a saka mu /Or throw us in deep wells
Ko a samu warin gwano/Or make us stink like black stink-ant
Daga hange sai leƙe sai ko harar nesa/Watching afar, hating with dirty looks
Wataran sai labari/It’d be all over one day
…
Ku san mai san ku/ Kana kusan mai ƙin ku/Know your fans/ Know your haters
Koda dare ko rana/ koda cikin ƙabari ne/Night or day, even in the grave
Koda ruwa ko iska/ koda cikin duhu ne/Through storms, even in the deepest darkness
Karyamaye, with full booming sound of 10 shantuna (pl.) with outside air energetically sucked down the aerophone provided a perfect percussion to their voices, and really demonstrated the power of the shantu in well-skilled hands. It is this rehearsed, almost flawless perfection that stood them better than other girl troupes in their immediate vicinity (e.g., Kurmin Mashi girls shantu troupe, also in Kaduna). Their verse was full of insouciance, defiance and pride in their art and identity; for instance:
Mu ƴan Hausa, da mu ƴan shantu/We, Hausa and shantu players
Perhaps, even aware of their delectable beauty, they cocked a snook at their unapproving but silent admirers:
Sai dai a gan mu a bar mu/ Sai ko hararar nesa/
The line is basically saying, look, but we are untouchable – you can only hate from afar. As I indicated earlier, the second performance, Alhaji Lawal Kalabayye, was named after the school’s food contractor, as confirmed by a former Home Economics teacher at the College, Mrs Lasfir Tasalla Andow, in 2019. The song, however, did not mention Alhaji Lawal himself, although the first lines of the song salute farmers – an obvious reference to food, and tangentially, to Alhaji Lawal!
Ina jin hausin mutumin ba ya zuwa gona/I am annoyed at a person who detests farming
Sai ya zauna a tsakar gida sai ka ce turmi/Always at home like some fixture
The song, however, further reaffirms the Hausa identity of the performers because they went through a cycle of profiling various ethnic groups – essentially pointing out the bad character traits of the groups, justifying their unwillingness to allow their daughters to marry them because of the profiled reasons they gave. For instance:
Ina da ƴata ni baza na bai wa Zagezagi ba/I will not marry off my daughter to Zaria people
Fate da safe, fate da yamma, kamar mayu/Yam porridge all day, like hexers
Ina da ƴata ni baza na bai wa Fulani ba/I will not marry off my daughter to the Fulani
Uwa a daji, uba a daji kamar kura/Both mother and father in wilderness, like hyenas
Ina da ƴata ni baza na bai wa Beriberi ba/I will not marry off my daughter to the Kanuri
Uwa da tsagu, uba da tsagu kamar ƙwarya/Both mother and father with facial marks, like calabashes
Ina da ƴata ni baza na bai wa Yoruba ba/I will not marry off my daughter to the Yoruba
Suna da kuɗi, amma a kwano suke kashi/They are wealthy, but they poop in their dishes
Ina da ƴata ni baza na bai wa Katsinawa ba/I will not marry off my daughter to Katsina people
Uwa masifa, uba masifa kamar sauro /Both the mother and father are too fiery, like mosquitoes
Ina da ƴata ni baza na bai wa malamin bana ba/I will not marry off my daughter to modern Malams
Yana wazifa, hannunsa na shafa ƴan mata/While being devotional, they also fondle little girls
These stereotypes, of course, fall within the purview of joking relationships in forms of playful taunts between citizens of various cities that made up the old kingdoms of northern Nigeria. Such relationships are often based on ancestral pacts forbidding conflict or war between specific communities, and imply that the members must love one another and provide assistance where needed. The lyrics were therefore not meant to condemn or belittle any community or groups.
It was surprising that Kano, with its almost manic commercialism, escaped this stereotyping – even though most of the girls were not from Kano, but perhaps their songwriters (most likely their Hausa subject teachers) were from, or affiliated with Kano! Whatever the case, their trenchant, non-politically correct lyrics cast them with an independent and spirited veneer that demands either acquiescence or indifference from the public. The ethnic groups of Yoruba, Kanuri and Fulɓe each came under their taunts. The Yoruba came into the picture because of Ilorin, considered one of the ‘bastard seven’ Hausa city-states (banza bakwai), although the historical narrative used Yoruba as a generic term; but it was only that Ilorin had a historical connection to the core Hausa states. Even respected Islamic teachers did not escape their barbs – – being accused of alleged sexual abuse of children under their care. This created a picture of betrayal of trust by those in charge of child care. Perhaps due to the constant radio criticisms of the girls by the cleric establishment in especially Kaduna and Kaduna, the performers felt obliged to point out that everyone has a bad spot, no matter how morally upright.
Alhaji Lawal Kalabayye ended with an acknowledgement of the support of their establishments in their art:
Teachers ku lura ku gane/Our teachers, be wary
Ƴan gulma suna nan/Gossipers abound
Yan baƙin ciki na nan/Haters are present
Gasunan dan su rabamu/Wanting to divide us
Wallahi baza su iya ba/By God, they will not succeed
They closed their performance with the song – and dance – that drew the ire of the public culture in northern Nigeria: Gantsare Gaye. The refrain was:
Gantsare gaye, gaye never go straight/
The sexual innuendo was clear in the ‘straight’ part of the chorus, and performing it in public took their art to a new level. The performance is available at https://bit.ly/3Eh0dYJ, with the ‘gantsarewa’ starting at tc1.01. ‘Gaye’ referred to what might be called ‘the dude’ – urban, transnational, metrosexual and sophisticated young man. Influenced by African American superstars such as Michael Jackson, young men in the north of Nigeria took to Jackson’s fashion and street cool. The Hausa ‘gaye’ (stylized from guy) was immortalized by the griot, Ɗan Maraya Jos in his song, ‘Ɗan Gaye Mugun Bawa’/The Badass.
Each of the girls was called out in the chorus to come and do the obscene gwatso dance – something that would probably make them blush later in their middle age years! Indeed, an unverified anecdote I once heard in Lagos decades after the event, was that one of the participating ladies phoned NTA requesting the TV station to stop repeated showing of the clip (which was part of archival cultural entertainment) because she said it was embarrassing.
The stage performance of Gantsare during the festival was more energetic than in the muted TV studio versions and an additional defiance to their critics – with total approval of their school.
Overall, regardless of the judgement on their performance, they did reflect an authentic female, and what I may even refer to as proto-teen feminist defiance. Certainly, the QAC girls had lent flair and elegance to a tradition of gendered performing art which counts as an intangible cultural heritage. Their granddaughters, by 2022, were the Gen Z cohort, and armed with TikTok, Snapchat and Instagram, rather than the shantu, carried the self-expression and defiance to a whole new level as petulant, entitled generation, and certainly without the cultural authenticity their grandmothers had.
Shantu Jazz Fusion and the Mezcal Jazz Unit
The Kano State History and Culture Bureau (HCB) subsequently established its own shantu troupe, made up of more mature ladies and keeping the spirit of intangible heritage alive. I had the opportunity to watch them perform live at the Emirates Palace Hotel, Abu Dhabi, UAE, on 1st October 2009 as part of the preparations to the conference on preservation of musical heritage of various cultures, Hausa being one of those chosen. I was with them in the dressing rooms backstage where I interviewed them, and later recorded their performance. A little bit of it is at https://bit.ly/3GBaSQG. A second Hausa act at the concert was Nasiru Garba Supa, who also performed, although without Fati and her shantu because by then Fati had left the band after getting married, although HCB retained her in some capacity.
Earlier in February 2009, the French Cultural Centre in collaboration with Alliance Française, Kano, organized a Kano Music Festival, Kamfest 2009. This was to bring French and Nigerian artists together for a three-day music festival. One of the French bands was Mezcal Jazz Unit, a jazz band formed in Montpellier, France. The band had established a reputation as being a fine jazz band and creating crossover fusion recordings with artists from various cultures worldwide.
The HCB shantu troupe was also featured at Kamfest 2009. While each band performed separately, a segment was created where a jam session was performed fusing MZU’s jazz improvisations with the HCB shantu sounds and vocals from the players. This creation must be seen as a real bridge between the two cultures via both authentic and peaceful exchanges, through music. Two cultures, two countries, one music!
Mezcal Jazz Unit, whose identity is maintained by regular confrontation with musical groups from all horizons, was one of the rare groups capable of engaging in smooth and fluid artistic collaborations that appear spontaneous. Their quartet was based on the clearly established principle of openness, allowing for a continuous invitation of “jazz” and “non-jazz” artists. This spirit inspired Mezcal Jazz Unit to formally record with the shantu ensemble in February 2009, just before the KAMFEST festival. The result was a CD, recorded in Kano, but mastered, pressed and marketed in Paris. The CD was simply titled Shantu. Released in 2010, it is available at https://apple.co/3zEMdGR, although some videos of the performance are also available at https://bit.ly/3DBDLcm.
Recently, the shantu has started coming back as part of female entertainment, especially during wedding ceremonies, as reflected in quite a few TikTok uploads of various shantu performances during ceremonies. Perhaps tired of the synthesizer love songs typical of modern Hausa singers (not musicians, since the singers rarely create the music accompanying their song) a revival of Hausa intangible cultural heritage is probably happening.
Preservation of the Hausa Intangible Cultural Heritage in Performing Arts
According to UNESCO, intangible cultural heritage includes the practices, representations, expressions, knowledge, skills – as well as the instruments, objects, artefacts and cultural spaces associated therewith – that communities, groups, in some cases, individuals recognize as part of their cultural heritage. Hausa female musical performance certainly are part of this heritage and is fast disappearing. There quite a few reasons for this.
First, music generally is frowned in Hausa societies. It is widely considered a low-class occupation (Smith has a good thought on this) – despite the immense popularity of both traditional griot and modern electronic (synthesizer) performing artists. This has the unpleasant outcome of relegating music and musicians to the background of any debate on social development.
Secondly, the subject matter of most musical performances also creates a distaste in the genre. With extremely few exceptions, Hausa performers are basically praise singers – singing the praises of politicians who pay them millions to praise them or denigrate their political opponents. This has contributed to lowering the image of musicians in the society. Rarely do musicians approach the art as an aesthetic process independent of client or patronage status.
Third, and mainly for women, public performance in predominantly Muslim communities is frowned upon because the audiences are not her muharrams – i.e., males with whom there is no possibility of any marriage. Salamatu Mai Gurmi, a female gurmi player, found a way around this by taking her husband along to her performances with his full permission. After all, the performances do put food on the table, as it were.
Fourth, the preservation of musical heritage requires a sustainable input in terms of concert dates, tours, record deals, publicity, distribution and marketing, etc., processes with not only required expertise that is absent among local, especially female, performers but also exposure – with attendant security risks – that will not make it possible for women to participate, no matter how talented. Currently, Barmani Choge’s female grandchildren have sustained their grandmother’s musical heritage in Funtua, Katsina State, but living in penury and lack of both individual and government support. I have instituted a project to get one of them to a studio and record her songs – which will be uploaded to YouTube for all to hear. Salamatu Mai Gurmi, from Bauchi, plays the gurmi on invitation to naming and wedding ceremonies, accompanied by her husband and playing to mainly female audience. She performed solely for the camera at https://bit.ly/3gkPKDS
Five, private female-only performances do take place in various places – for instance, the Sakaina (broken calabash as instruments) performance in the Kano Emir’s Palace in the past. However, such performances are not public, even though they are part of the intangible heritage to be preserved. There is a need to create public equivalents, even if restricted to private female audiences, of these performances, especially among older women.
As we focus on the preservation of the Intangible Cultural Heritage in the performing arts domain of the Muslim Hausa female, the main thrust of such preservation falls on the National Institute of Cultural Orientation (NICO), a UNESCO country partner representing the Federal Ministry of Information and Culture.
Thus, NICO can sustain its revival movements as a form of cultural activism that uses elements from the past to legitimate change—change comprising not only a reversion to past practices but innovation. Therefore, a series of initiatives are needed to preserve the intangible heritage of the shantu performance.
The Institute could initiate a policy dialogue involving public culture representatives – clerics, youth organizations, community leaders – that will fashion out an acceptable re-insertion of shantu music as accepted public performance. This is because the issue of the public visibility of the female within Islam has to be balanced out. Of course, there are many young women in Hausa societies who are currently performing as singers (though not as musicians) in the public domain. Yet, traditional instruments, in the hands of women and in public arena does tend to rub some people in the Islamicate culture of northern Nigeria the wrong way. Dialogue is critical to everyone being on the same page.
At the same time, NICO could institute a competition among girls and young women and clustered by age for shantu playing, with prizes for the best three within each group. The songs needed not be on relationships – they could over all spectrum of human behavior, with prizes awarded for the best performance in each category – and such rewards to include marketing and promotion of the output.
Finally, the success of the crossover genre embarked by the Mezcal Jazz Unit and shantu clearly points to the future of such crossover improvisations. For instance, amada performers can be integrated with both shantu and gurmi players for a series of fusion concerts. This will create new innovations in Hausa female music and certainly provide a welcome alternative and exposure to a performance genre that is fast being smothered by synthesized sounds.
Select Bibliography
Adamu, Abdalla Uba. “Tribute to Hajiya Sa’adatu Ahmad Barmani Choge, Griotte, northern Nigeria, 1948-2013.” The Annual Review of Islam in Africa, University of Cape Town, South Africa, Issue No. 12/13, pp. 166-172, 2016.
Adamu, Abdalla Uba. “Womanist ethos and Hausa domestic ecology: A structuralist analysis of Barmani Choge’s operetta, Sakarai ba ta da wayo (Useless woman).” In S. Abdu (Ed.). Poetry and Poetics: Proceedings of the 5th Conference on Literature in Northern Nigeria. Bayero University Kano: Department of English and French, pp. 93-120, 2008.
Almajir, Tijjani Shehu. 2022. Sigogin Waƙoƙin Shantu da Tasirinsu a Rayuwar Hausawa. Bayero University Kano. Kadarkon Adabin Hausa: A Festschrift in Honour of Professor Sa’idu Muhammad Gusau. Forthcoming, 2023.
Ames David Wason and King, Anthony V. Glossary of Hausa Music and Its Social Contexts. Northwestern University Press, 1971.
Ames, David Wason. “Professionals and Amateurs: The Musicians of Zaria and Obimo.” African Arts, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 40-45+80+82-84, 1968.
DjeDje, Jacqueline Cogdell. “West Africa: An Introduction.” In Ruth Stone (Ed.). The Garland Handbook of African Music. New York: Routledge, pp. 166-197, 2000.
DjeDje, Jacqueline Cogdell. Fiddling in West Africa: Touching the Spirit in Fulɓe, Hausa, and Dagbamba Cultures. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2008.
Erlmann, Veit. “Notes on Musical Instruments among the Fulani of Diamare (North Cameroon).” African Music: Journal of the International Library of African Music, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 16-41, 1983. https://doi.org/10.21504/amj.v6i3.1166.
Jatau, Phoebe. “Shantu Songs: An Example of the Oral Heritage of Hausa Women in Kaduna State.” In Saleh Abdu and Muhammad Badmus (eds.), Writing, Performance and Literature in Northern Nigeria. 2nd ed. Kano: Bayero University Press, pp.166-182, 2006.
Kassam, Margaret Hauwa. “Some Aspects of Women’s Voices from Northern Nigeria.” African Languages and Cultures, vol. 9, no. 2, Gender and Popular Culture, pp. 111-125, 1996.
Kofoworola, Ziky and Yusef Lateef. Hausa Performing Arts and Music. Lagos, Nigeria: Department of Culture Federal Ministry of Information and Culture, 1987.
Mack, Beverly Blow. Muslim Women Sing. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2004.
MacKay, Mercedes. “The Shantu Music of the Harims of Nigeria.” African Music: Journal of the African Music Society, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 56–57, 1955. https://doi.org/10.21504/amj.v1i2.255.
Musa, Umma Aliyu. “Promoting women empowerment through songs: Barmani Choge and her performances.” Journal of African Languages and Literatures, vol.1, 2020, pp.89-109, https://doi.org/10.6092/jalalit.v1i1.6735.
Smith, Michael Garfield. “The Hausa System of Social Status.” Africa, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 239–252, 1959.